pH Electrode with CPS™ for Non-aqueous Titrations - HI1049B
- Clogging Prevention System (CPS™) Technology
- Double Junction Design
- Refillable Electrode
Hanna Instruments offers a wide variety of pH electrodes that are designed for many different applications. The type of glass used for sensing pH, bulb shape, body material, type of junction, type of reference and electrolyte used are just some of the design considerations. The HI1049B uses general purpose (GP) glass, spherical bulb, glass body, sleeve junction with CPS™ technology, double junction and is refillable with 3.5M KCl, making it ideal for samples with a high solids content.
General Purpose Glass Formulation
General Purpose (GP) glass, as the name implies, is a standard glass formulation that is used for general use. A pH electrode with GP glass will have a resistance of 100 megaohms at 25°C and is suited for measuring the pH of samples that are at ambient temperatures. The HI1049B is suitable to use with samples that measure from 0 to 80°C.
Spherical Glass Tip
The spherical shaped tip design allows for a wide area of contact with the measured sample. This permits a faster electrode response with a higher degree of stability.
CPS Sleeve Junction
Clogging Prevention System (CPS) technology is an innovation in for the improvement of pH measurements in samples that have a high solids content. Conventional pH electrodes use ceramic junctions that can clog quickly when used in samples that have a high solids content. When the junction is clogged, the electrode does not function. CPS technology utilizes the porousness of ground glass coupled with a PTFE sleeve to prevent clogging of the junction. The ground glass allows the proper flow of the liquid, while the PTFE sleeve repels solids. As a result, pH electrodes with CPS technology take up to 20 times longer to be fouled as compared to conventional electrodes.
Double Junction Reference
A double junction electrode has an internal compartment surrounding the reference wire. Silver ions are present in the electrolyte of the internal compartment, which houses the Ag/AgCl reference wire; the electrolyte outside this compartment is silver free. The double junction design means that virtually no silver from the electrode enters the sample. This design allows measurement in applications where silver ions in the sample are undesirable or for samples that contain sulfides that can cause the silver to precipitates and clog the junction. The clogging of the junction will result in drifty and erratic readings.
Refillable
The HI1049B is a refillable probe. Since it is a double junction pH electrode, the fill solution is the HI7082 3.5M KCl. This solution does not contain any silver as with single junction electrode fill solutions.
Glass Electrode Body
The glass body is ideal for laboratory use. The glass is resistant to many harsh chemicals and is easily cleaned. The glass body also allows for a fast transfer of heat to the internal reference electrolyte. The mV generated by the reference cell is temperature dependent. The faster the equilibrium the steadier the reference potential.
BNC Connector
The HI1049B has a BNC connector. This type of connector is universal in that it can be used on any pH meter that has a female BNC probe input. Other types of connectors include DIN, screw type, T-type, and 3.5mm to name a few. These types of connectors tend to be proprietary for a particular type of meter and are not interchangeable.
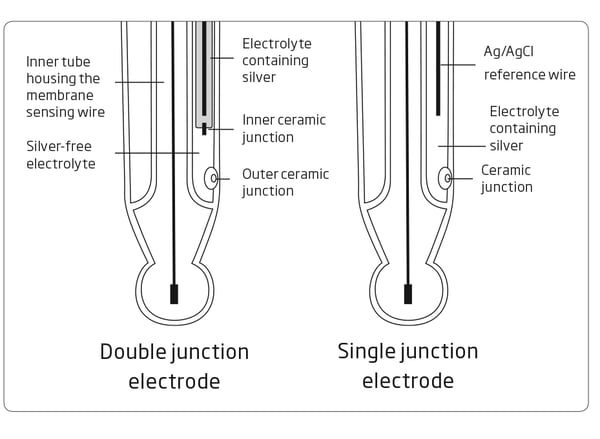
Single Junction Versus Double Junction pH Electrodes
Conventional electrodes are normally single junction. As depicted by the figure above, these electrodes have only a single junction between the internal reference wire and the external solution. Under adverse conditions, such as high pressure, high temperature, highly acidic or alkaline solutions, the positive flow of the electrolyte through the junction is often reversed resulting in the ingress of sample solution into the reference compartment. If this is left unchecked, the reference electrode can become contaminated, leading to complete electrode failure. Another potential problem with single junction electrodes is the clogging of the junction due to silver chloride (AgCl) precipitation. Silver can be easily precipitate in samples that contain Tris buffer or heavy metals. When the electrolyte solution makes contact with the sample, some AgCl will precipitate on the external face of the junction. The result is drifty readings obtained from the sensor. Hanna’s double junction system, as the name implies, has two junctions, only one of which is in contact with the sample as shown in the figure. Under adverse conditions, the same tendency of sample ingress is evident. However, as the reference electrode system is separated physically from the intermediate electrolyte area, the contamination of the electrode is minimized. The likelihood of clogging of the junction is also reduced with a double junction electrode since the outer reference cell uses a fill solution that is “silver-free”. Since there is no silver present, there is no precipitate forming to clog the junction.
Specifications
| Specification Name | Detail |
|---|---|
| SKU | HI1049B |
| Description | pH electrode with CPS™ (Clogging Prevention System) |
| Reference | double, Ag/AgCl |
| Junction / Flow Rate | CPSTM |
| Electrolyte | KCl 3.5M |
| Max Pressure | 0.1 bar |
| Range | pH: 0 to 12 |
| Recommended Operating Temperature | -5 to 80°C (23 to 176°F) |
| Tip / Shape | dome (dia: 8 mm) |
| Temperature Sensor | no |
| Amplifier | no |
| Body Material | glass |
| Cable | coaxial; 1 m (3.3’) |
| Recommended Use | non-aqueous titrations |
| Connection | BNC |